A Critical Time to Treat
In the United States, obesity is a public health crisis1
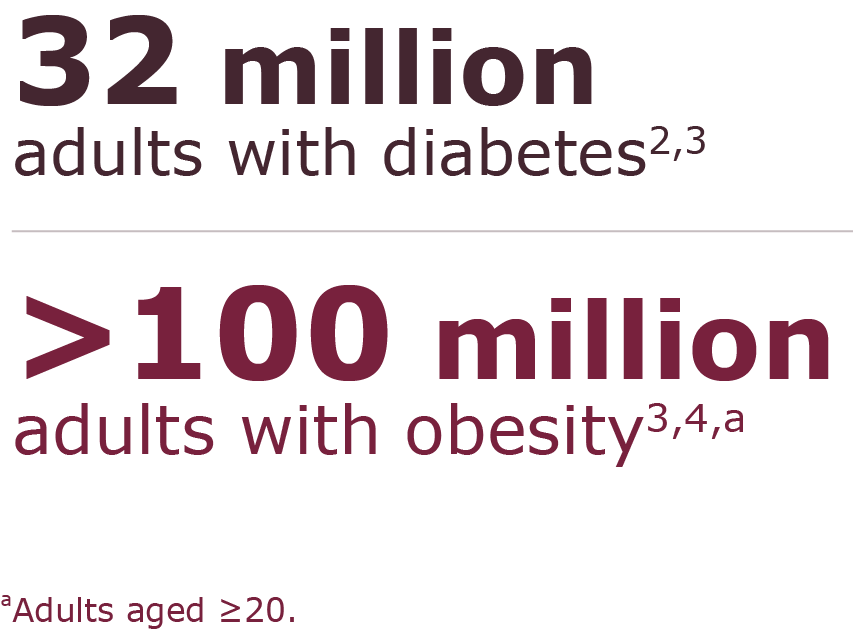
Obesity has been recognized as a disease by leading medical organizations, including5-10:
- American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE)
- American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP)
- American Medical Association (AMA)
- The Obesity Society (TOS)
- World Obesity Federation (WOF)
Obesity may be a contributing factor to many health risks
Obesity may be a contributing factor to many health risks


Why Treat? Even Weight Loss of 5% or More Is Clinically Meaningful12
Obesity should be treated in a chronic manner similar to common comorbidities such as dyslipidemia and hypertension8
Treating obesity is important for many reasons, one of which is its effect on cardiometabolic risk factors. Studies have shown weight loss of 5% or more to have an impact on cardiometabolic risk factors, including12:
Blood pressure
Cholesterol levels
Triglyceride levels
Saxenda® is not indicated for the treatment of hypertension or dyslipidemia.
RECOMMENDED CONTENT
Saxenda® can help patients get closer to their weight-loss goals
Important Safety Information for Saxenda® (liraglutide) injection 3 mg
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
Liraglutide causes dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures in both genders of rats and mice. It is unknown whether Saxenda® causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans, as the human relevance of liraglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined.
Saxenda® is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC and in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Counsel patients regarding the potential risk of MTC with use of Saxenda® and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (eg, a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness). Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with Saxenda®.
Indications and Usage
Saxenda® (liraglutide) injection 3 mg is indicated as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for chronic weight management in:
- Adult patients with an initial body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or greater (obese) or 27 kg/m2 or greater (overweight) in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition (eg, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or dyslipidemia)
- Pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with body weight above 60 kg (132 lbs) and initial BMI corresponding to 30 kg/m2 or greater for adults (obese) by international cut-offs
Limitations of Use
- Saxenda® contains liraglutide and should not be coadministered with other liraglutide-containing products or with any other GLP-1 receptor agonist
- The safety and effectiveness of Saxenda® in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes have not been established
- The safety and effectiveness of Saxenda® in combination with other products intended for weight loss, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter drugs, and herbal preparations, have not been established
Important Safety Information cont.
Contraindications
Saxenda® is contraindicated in:
- Patients with a personal or family history of MTC or patients with MEN 2
- Patients with a serious hypersensitivity reaction to liraglutide or to any of the excipients in Saxenda®. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported with Saxenda®
- Pregnancy
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors: If serum calcitonin is measured and found to be elevated, the patient should be further evaluated. Patients with thyroid nodules noted on physical examination or neck imaging should also be further evaluated
- Acute Pancreatitis: Acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis, has been observed in patients treated with liraglutide postmarketing. Observe patients carefully for signs and symptoms of pancreatitis (persistent severe abdominal pain, sometimes radiating to the back with or without vomiting). If pancreatitis is suspected, discontinue Saxenda® promptly and if pancreatitis is confirmed, do not restart
- Acute Gallbladder Disease: Substantial or rapid weight loss can increase the risk of cholelithiasis; however, the incidence of acute gallbladder disease was greater in patients treated with Saxenda® than with placebo even after accounting for the degree of weight loss. If cholelithiasis is suspected, gallbladder studies and appropriate clinical follow-up are indicated
- Hypoglycemia: Adult patients with type 2 diabetes on an insulin secretagogue (eg, a sulfonylurea) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia with use of Saxenda®. The risk may be lowered by a reduction in the dose of insulin secretagogues or insulin. In pediatric patients without type 2 diabetes, hypoglycemia occurred. Inform all patients of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms
- Heart Rate Increase: Mean increases in resting heart rate of 2 to 3 beats per minute (bpm) were observed in patients treated with Saxenda®. Monitor heart rate at regular intervals and inform patients to report palpitations or feelings of a racing heartbeat while at rest during treatment with Saxenda®. Discontinue Saxenda® in patients who experience a sustained increase in resting heart rate
- Renal Impairment: Acute renal failure and worsening of chronic renal failure, which may sometimes require hemodialysis, have been reported, usually in association with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or dehydration. Use caution when initiating or escalating doses of Saxenda® in patients with renal impairment
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (eg, anaphylaxis and angioedema) have been reported in patients treated with Saxenda®. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, patients should stop taking Saxenda® and promptly seek medical advice
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation: In adult clinical trials, 9 (0.3%) of 3,384 patients treated with Saxenda® and 2 (0.1%) of the 1,941 treated with placebo reported suicidal ideation; one of the Saxenda® treated patients attempted suicide. In a pediatric trial, 1(0.8%) of the 125 Saxenda® treated patients died by suicide. There was insufficient information to establish a causal relationship to Saxenda®. Monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Discontinue treatment if patients experience suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Avoid Saxenda® in patients with a history of suicidal attempts or active suicidal ideation
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions, reported in ≥5% are nausea, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, injection site reactions, headache, hypoglycemia, dyspepsia, fatigue, dizziness, abdominal pain, increased lipase, upper abdominal pain, pyrexia, and gastroenteritis
Drug Interactions
- Saxenda® causes a delay of gastric emptying and has the potential to impact the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Monitor for potential consequences of delayed absorption of oral medications concomitantly administered with Saxenda®
Use in Specific Populations
- There are no data on the presence of liraglutide in human breast milk; liraglutide was present in the milk of lactating rats
- Saxenda® has not been studied in patients less than 12 years of age
- Saxenda® slows gastric emptying. Saxenda® has not been studied in patients with preexisting gastroparesis
Please click here for Saxenda® Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning.
References
1. Wang Y, Beydoun MA, Liang L, Caballero B, Kumanyika SK. Will all Americans become overweight or obese? Estimating the progression and cost of the US obesity epidemic. Obesity. 2008;16(10):2323-2330.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2017. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2017.
3. US Census Bureau. QuickFacts: United States. Accessed July 19, 2022. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US#viewtop
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Obesity and overweight. Accessed July 19, 2022. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/obesity-overweight.htm
5. Guh DP, Zhang W, Bansback N, Amarsi Z, Birmingham CL, Anis AH. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. 2009;9:1-20.
6. Garvey WT, Mechanick JI, Einhorn D. The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology: 2014 advanced framework for a new diagnosis of obesity as a chronic disease. Endocr Pract. 2014;20(9):977-989.
7. Overweight, obesity, and fitness. American Academy of Family Physicians. Accessed July 20, 2021. https://www.aafp.org/family-physician/patient-care/prevention-wellness/healthy-lifestyle/obesity-activity.html
8. Bray GA, Kim KK, Wilding JPH. Obesity: a chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes Rev. 2017;18(7):715-723.
9. What is obesity? The Obesity Society. Updated April 2016. Accessed November 5, 2019. https://www.obesity.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Jastreboff_et_al-2019-Obesity.pdf
10. Frellick M. AMA declares obesity a disease. Medscape. Accessed November 17, 2019. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/806566
11. Bays HE, Seger JC, Primack C, et al. Obesity algorithm 2017-2018. Presented by the Obesity Medicine Association. Accessed July 21, 2022. https://obesitymedicine.org/obesity-algorithm
12. Wing RR, Lang W, Wadden TA, et al; Look AHEAD Research Group. Benefits of modest weight loss in improving cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(7):1481-1486.